Student Essays Grades Prediction
a project using DeBerta and other transformers
Motivation and goal
The group of students learning English as a second language, known as English Language Learners (ELLs), has rapidly grown. While automated feedback tools make it easier for teachers to assign more writing tasks, they are not designed with ELLs in mind. Existing tools are unable to provide feedback based on the language proficiency of the student, resulting in a final evaluation that may be skewed against the learner. We hope to improve automated feedback tools to better support the unique needs of these learners. Our goal is to utilize a dataset of essays written by ELLs to develop English language proficiency evaluation models, which help ELLs receive more accurate feedback on their language development and expedite the grading cycle for teachers.
Dataset
The dataset (the ELLIPSE corpus) comprises argumentative essays written by 8th-12th grade ELLs. The essays have been scored according to six analytic measures: cohesion, syntax, vocabulary, phraseology, grammar, and conventions. Each measure represents a component of proficiency in essay writing, with greater scores corresponding to greater proficiency in that measure. The scores range from 1 to 5 in increments of 0.5. Our task is to predict the scores for each of the six measures for the essays in the test set with train test split 80 : 20.
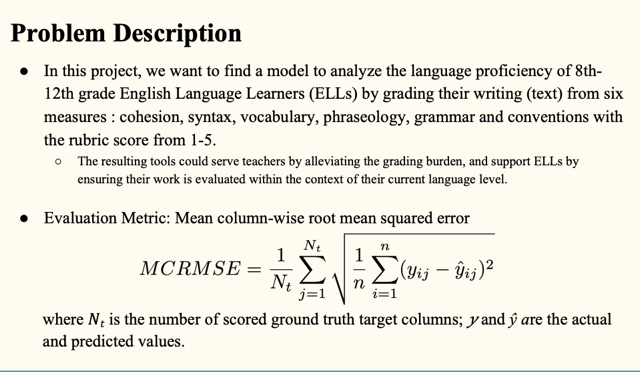
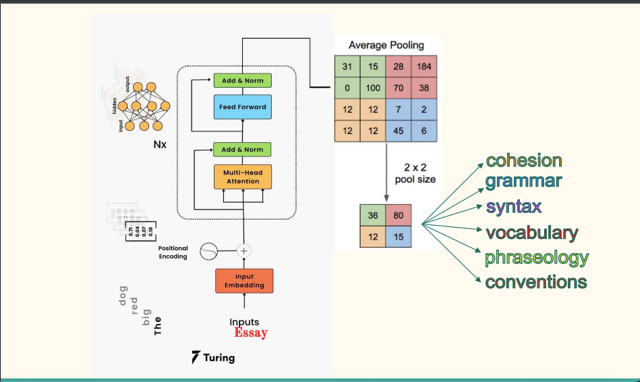
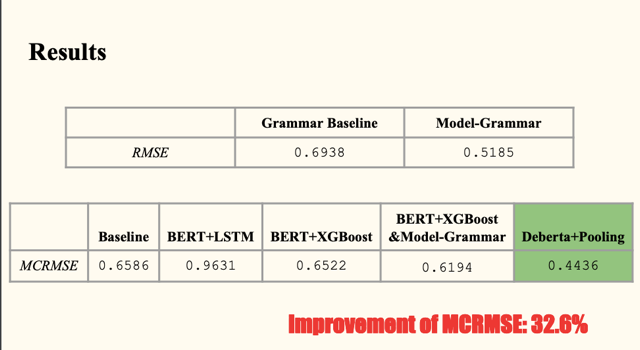
Methodology Our evaluation metric is the mean column-wise root mean squared error (MCRMSE). We use the mean score of each analytic measure from the train set as our baseline. Firstly, we use pretrained BERT to train through partial LSTM decoder and dense output layer. Secondly, we try pretrained BERT plus XGBoost regression. In addition, we propose a model tailored to the grammar measure. We first train a BERT model on the Corpus of Linguistic Acceptability (CoLA) dataset, and then use this pretrained model as a single sentence grammar checker to obtain ratios of grammatically correct sentences for the essays, and lastly use the preprocessed data to train against grammar measure through XGBoost regressor. Next, we replace the grammar column training in the second model with this proposed grammar model. Finally, we train DeBERTa model using its disentangled attention mechanism, apply mean pooling on the last hidden state and then add dense output layer.